The Rib Cage Riddle: Exploring the Anatomy of Men’s Ribs
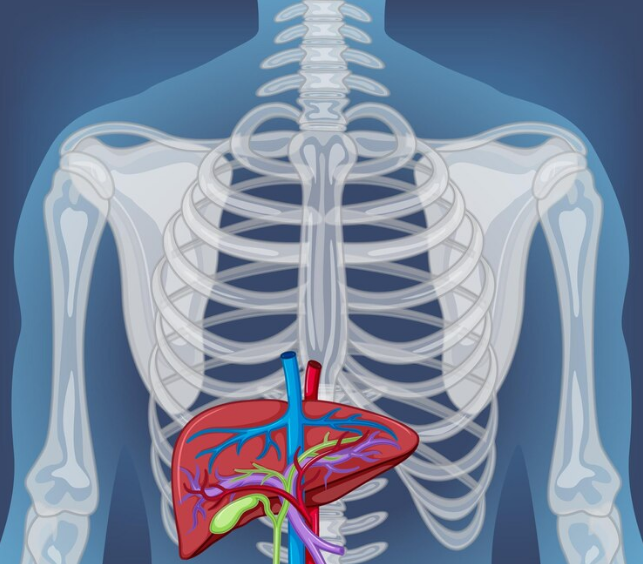
In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the intricate world of men’s rib anatomy. The human rib cage is a fascinating structure that not only protects vital organs but also plays a significant role in maintaining posture and facilitating respiration. Join us on this journey as we uncover the mysteries of the rib cage.
Introduction: Deciphering the Rib Cage
The rib cage, also known as the thoracic cage, is a bony and cartilaginous structure that forms the chest wall. It comprises several key elements, including rib, sternum, and cartilage. Understanding the components of the rib cage is crucial to grasping its significance in human anatomy.
The Structure of Ribs
To comprehend the rib cage fully, we must start by examining the rib themselves. Rib are long, curved bones that make up the framework of the chest. There are 12 pairs of rib in the human body, and they are categorized into three types:
True Ribs (Vertebrosternal Ribs)
True rib are the first seven pairs of rib, and each of them is directly attached to the sternum by costal cartilage. These rib provide structural support to the anterior chest wall.
False Ribs (Vertebrochondral Ribs)
The next three pairs of ribs, from the 8th to the 10th, are classified as false ribs. They connect to the sternum indirectly through the cartilage of the preceding rib, giving them a less direct attachment.
Floating Ribs (Vertebral Ribs)
The last two pairs of rib, the 11th and 12th, are known as floating ri. Unlike the true and false rib, they do not attach to the sternum at all, making them unique in the rib cage structure.
The Sternum: The Keystones of the Ribs Cage
The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat, elongated bone located at the center of the chest. It consists of three parts:
Manubrium
The manubrium is the uppermost part of the sternum and connects to the clavicles. It provides a stable anchor for the first pair of rib.
Body
The body of the sternum also called the gladiolus, forms the bulk of the bone and articulates with the costal cartilages of the true rib.
Xiphoid Process
The xiphoid process is the smallest and most inferior part of the sternum. It may vary in shape and size among individuals.

The Function of the Rib Cage
Understanding the anatomy of the rib cage is only half the puzzle. To appreciate its significance, we must explore its functions:
Protection of Vital Organs
One of the primary functions of the rib cage is to protect vital organs, including the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. The ribs act as a sturdy shield against external trauma.
Support for Respiration
The rib cage plays a pivotal role in the mechanics of breathing. During inhalation, the rib cage expands, creating a vacuum in the thoracic cavity, which draws air into the lungs. Exhalation, on the other hand, involves the relaxation of the rib cage.
Postural Support
Maintaining an upright posture is made possible by the rib cage. It provides structural support for the spine and keeps the body in an optimal position for various activities.
Hematopoiesis
Red bone marrow within the ribs is responsible for the production of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This process, known as hematopoiesis, is vital for overall health.
The Rib Cage in Perspective
To put the complexity of the rib cage into perspective, consider it as the body’s natural armor, responsible for safeguarding vital organs and facilitating essential functions like breathing and posture. While it might seem straightforward, this intricate structure has fascinated anatomists for centuries.
Conclusion
The ribs cage, with its interplay of ribs, sternum, and cartilage, is an indispensable part of human anatomy. It serves not only as a protective shield but also as a key player in the mechanics of respiration and postural support. Understanding the ribs cage’s anatomy and functions sheds light on its vital role in our overall well-being.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Are men’s and women’s ribs cages the same?
No, there are subtle differences between the ribs cages of men and women. Men tend to have larger and broader ribs cages, while women’s ribs cages are typically smaller and narrower.
2. Can rib fractures be serious?
Yes, rib fractures can be serious, especially if they puncture the lungs or damage nearby organs. They can cause significant pain and difficulty breathing.
3. How can I maintain a healthy ribs cage?
Maintaining a healthy ribs cage involves regular exercise to strengthen the muscles surrounding it. Proper posture and avoiding activities that could lead to trauma are also essential.
4. Can the ribs cage change in shape over time?
Yes, the ribs cage can change in shape due to factors like aging, injury, or certain medical conditions. It is essential to monitor any significant changes and consult a healthcare professional if necessary.
5. Is it possible to increase lung capacity by exercising the ribs cage?
While exercise can improve lung function to some extent, lung capacity is primarily determined by genetics. However, exercises that promote lung health can be beneficial for overall well-being.


